The ITU Academy uses mainly Articulate 360 software for interactive self-paced materials. There are two possible software options:
- Rise 360: to create simple text-based modules with some elements of interactivity (drag and drop cards, carousels etc.).
- Storyline 360: to create complex animated and/or voice-based lectures with more interactive elements.
Whether the instructional designer is hired as an individual or as a vendor through the LTA, they work together with the course coordinator, and subject matter experts, if necessary, to design the interactive content.
The graphic below outlines the iterative process and deliverables of the instructional designer:
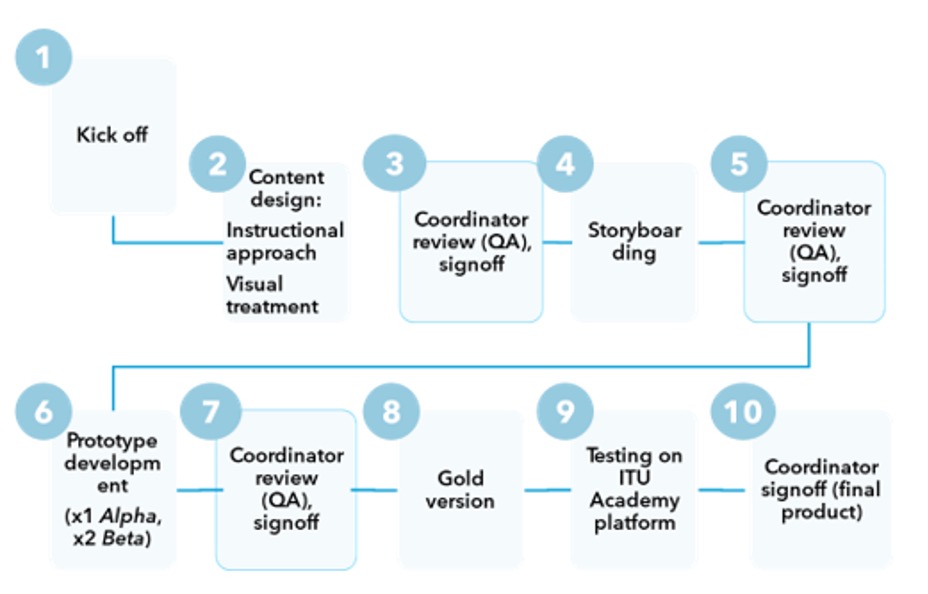
The process is described in the table below. See the full:
for information related to the procurement process to hire vendors through the LTA.
| Phase | Stage | Description | Outcome | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DESIGN | 1. Kick off | Clarifies roles and responsibilities (Subject-Matter Expert (SME), Course coordinator etc.), project scope, target audience requirements, learning objectives and evaluation, review cycles, technology details, budget constraints, timelines, localisation approach, learning platform treatment. | Project initiation document, Project plan | |
| 2. Instructional approach | Meeting(s) to establish how the content will be organized (chapters, module map), what style to use, tone, etc. It results in a high-level plan of the overall approach for the course. It also ensures the Instructional Designer (ID) has a good grasp of the content. | High level design document | ||
| 3. Visual treatment | A short consultation stage to agree on course look and feel, appearance, branding, graphics. Narration voices & tone may also be discussed. | Mock-ups, mood board, course player | ||
| 4. Storyboarding | This is essentially the blueprint for the course. The storyboard presents the on-screen text, audio elements, and interactivities. It details what participants will see, hear, and do during the course. It sets the expectations for content treatment and is used throughout the development phase as the guide for building the course. Review: it is essential that the storyboards capture the content/text in its final form! | Finalized and detailed script for the course (critical review stage!) | ||
| DEVELOPMENT | 6. Prototype | Alpha version | A draft on-screen version of the course, created in the selected authoring tool. The purpose of this deliverable is to give the client a realistic preview of how the course will flow. Narration (if present) is not in its final form and many of the images are placeholder images. Most interactivities are inserted at this stage. Review: medium content/wording adjustments, audio and interaction modifications possible. Final edits should be requested in this stage of the prototype! | Beta version (critical review stage!) |
| Beta version | An on-screen advanced prototype version of the course, adjusted based on the corrections and changes requested by the client during Alpha review. Contains final narration (if applicable), images and media assets (animations, videos). Review: very limited final tweaks (punctuation, etc.). No new content requests/additions possible. Bigger changes usually incur extra costs and additional production time. | Gold version (critical review stage!) | ||
| 8. Gold version | The final format of the course, a fully developed module in which all of the activities have been adjusted based on the corrections requested by the client in Alpha and Beta. | SCORM package (LMS compliant) | ||
| DEPLOYMENT | 9. Testing on the ITU Academy platform | Technical quality assurance stage to confirm that the course functions properly on the ITU learning platform (launch, completion, tracking). | Course added to catalogue | |